The Essentials of Discrete Manufacturing in SAP PP

Introduction
In the intricate landscape of manufacturing, challenges abound, and solutions are sought after more than ever. Do you find yourself pondering over the complexities of production planning, resource optimization, and efficient inventory management? If so, you’re not alone. The manufacturing world is evolving, and solutions are at the forefront.
Are You Curious to know what’s the solution is?
Discrete Manufacturing in SAP PP (Production Planning) —a realm where final goods are composed of distinct parts, easily counted, touched, and seen. Whether you’re crafting automobiles, furniture, airplanes, toys, or smartphones, you face unique challenges.
How do you align inventory with fluctuating demand?
Can you efficiently manage resources while maintaining top-notch quality? —The answer lies in the realm of discrete manufacturing.
Now, having explored the intricacies of discrete manufacturing, let’s transition to the solution that empowers industries to navigate these complexities with finesse—SAP PP, the Production Planning module within the SAP S/4HANA system is tailored to address the unique challenges of discrete manufacturers.
Let’s unravel how SAP PP optimizes production planning, resource allocation, and quality control in the realm of discrete manufacturing.
Introducing SAP PP: Your Solution in Discrete Manufacturing
Production planning is the backbone of any successful business, and SAP PP is a vital module within the SAP ERP system that plays a key role in ensuring efficient production processes.
Now, let’s dive into the essentials of SAP PP, with a focus on discrete manufacturing, one of the three manufacturing processes.
The significance of production planning cannot be overstated. Effective production planning aims to maximize profits by optimizing processes, reducing inventory costs, and efficiently utilizing resources and equipment.
Production Planning Significance
Production planning is a crucial aspect of any manufacturing business. It involves aligning the demand for products with the available manufacturing capacity. SAP PP is designed to facilitate this alignment by providing tools and processes to efficiently manage and optimize production operations. Its significance lies in:
- Maximizing Profits:
Effective production planning can help maximize profits by ensuring that products are manufactured efficiently, reducing costs, and optimizing the use of resources and equipment.
- Inventory Management:
SAP PP aids in minimizing excess inventory by ensuring that production aligns with demand, preventing overproduction, and reducing carrying costs.
- Resource Optimization:
It helps in optimizing the utilization of resources such as machines, labor, and materials, resulting in better resource management.
Integration with Other SAP Modules
SAP PP doesn’t work in isolation; it integrates seamlessly with other SAP modules:
- Sales and Distribution (SD):
Integration with SD allows for a smooth flow of information from sales orders to production planning. It ensures that production responds to customer demand.
- Material Management (MM):
Integration with MM enables efficient management of raw materials and components needed for production.
- Financial Management (FICO):
Integration with FICO ensures that financial data related to production, including costs and revenues, are accurately recorded and tracked.
- Plant Maintenance (PM):
PM integration helps in maintaining machines and equipment, ensuring they are in optimal condition for production.
- Logistics Execution (LE):
Integration with LE streamlines logistics processes like transportation and warehousing.
Discrete Manufacturing in SAP PP
Discrete manufacturing is characterized by:
- Production Orders:
Production orders are the foundation of planning and execution in discrete manufacturing. They define what needs to be produced, in what quantity, and on which resources.
- Frequent Product Changes:
Discrete manufacturing often involves products that can be easily customized or reworked. The ability to adapt to changes is a key feature.
- Material Issuance:
Materials are typically issued with reference to production orders, ensuring accurate tracking of material consumption.
- Master Data Utilization:
Master data elements such as work centers, production versions, routing, and BOMs are critical for configuring and executing production processes efficiently.
Master Data in SAP PP
In SAP PP, master data plays a crucial role:
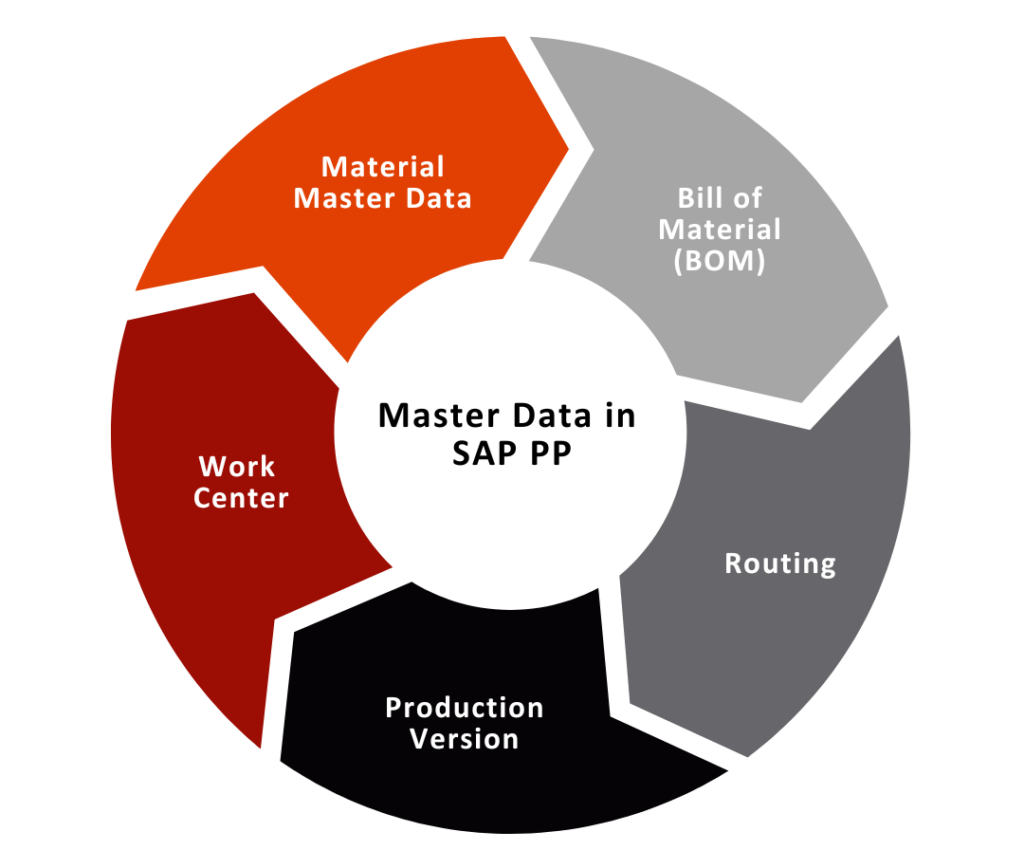
- Material Master Data:
This central source of information contains details of materials and is used across various departments, including Sales, Purchasing, Finance, and Production Planning.
- Bill of Material (BOM):
BOM lists the materials, components, and their quantities required for assembly or sub-assembly, guiding the manufacturing process.
- Work Center:
Work centers store data related to scheduling, capacity, and costing. They typically represent machines or groups of machines used in production.
- Routing:
Routing defines the sequence of operations performed at work centers. It’s essential for tracking machine and labor costs and calculating standard material costs.
- Production Version:
Multiple production versions may exist for different manufacturing processes of a product. It helps determine the specific manufacturing process to be followed.
The Production Planning Process
At its core, production planning involves aligning demand with manufacturing capacity to achieve production goals. It encompasses creating schedules for both finished and raw materials, documenting and tracking manufacturing processes, and monitoring planned vs. actual costs. Additionally, it tracks the movement of goods from raw materials to semi-finished or finished products.
The production planning process involves several key steps:
- Demand Forecasting:
Understanding the demand for products is the first step. SAP PP helps in creating forecasts based on historical data and market trends.
- Master Data Management:
SAP PP relies on accurate master data, including the Material Master, Bill of Materials (BOM), Work Centers, Routing, and Production Versions. These data elements provide detailed information about materials, components, production sequences, and resource availability.
- Planning Strategies:
SAP PP offers different planning strategies, including Make-to-Stock (MTS) and Make-to-Order (MTO).
* Make to Stock (MTS): This involves producing goods without specific sales orders and maintaining ready stock in the plant.
* Make to Order (MTO): In this case, production begins only after receiving specific sales orders for a particular material
- MRP (Material Requirements Planning):
MRP in SAP PP calculates material requirements based on the demand forecast, bill of materials, and lead times. It generates planned orders for materials that need to be procured or produced.
- Capacity Planning:
This step ensures that production resources (such as machines and labor) are available when needed. SAP PP helps in capacity planning to avoid bottlenecks and optimize resource utilization.
- Production Scheduling:
Once capacity planning is done, production orders are scheduled. SAP PP considers factors like resource availability, lead times, and priority to create production schedules.
Execution of SAP PP in Discrete Manufacturing
In the execution phase:
- Planned Orders to Production Orders:
Planned orders, generated during planning, are converted into production orders. These orders contain detailed instructions for production, including routing information.
- Material Availability:
SAP PP checks the availability of materials required for production. If materials are not available, it generates purchase requisitions or production orders to acquire them.
- Production:
The actual production process occurs according to the routing and work center instructions. Labor and machine hours are recorded to track production costs.
- Confirmation and Delivery:
After production is complete, confirmation of the orders is done. The products are then delivered to customers as per sales orders or stocked in the inventory.
In conclusion
SAP PP is a comprehensive module that empowers manufacturing businesses to streamline their operations, align production with demand, optimize resources, and control costs effectively. Discrete manufacturing, one of the supported manufacturing types, is particularly suited for industries with valuable demand and products that can be customized easily. By harnessing the power of SAP PP, companies can position themselves for success in today’s competitive manufacturing landscape.
If you have any queries or guidance contact us at KaarTech.
FAQ’s
Why SAP PP for discrete manufacturing?
SAP PP (Production Planning) is a crucial module within SAP S/4HANA, specifically tailored for discrete manufacturing. It addresses challenges in production planning, resource allocation, and quality control.
How does SAP PP optimize production planning?
SAP PP maximizes profits, minimizes excess inventory, and optimizes resource utilization. It aligns demand with manufacturing capacity, ensuring efficient production processes and cost-effective operations.
What is the significance of master data in SAP PP?
Master data elements such as Material Master, BOM, Work Center, Routing, and Production Version play a crucial role in SAP PP. They provide detailed information about materials, components, production sequences, and resource availability.
What are the key steps in the SAP PP production planning process?
The production planning process involves demand forecasting, master data management, planning strategies (MTS and MTO), MRP, capacity planning, and production scheduling. SAP PP ensures alignment of production goals with demand and efficient resource utilization.
